ESG investing
Environmental, Social & Governance (ESG) information describes how responsibly a business is managed by showing how its operations affect its most material stakeholders such as its customers and employees or the environment. ESG data is now widely integrated by investment managers because it helps them understand material risks and opportunities that are associated with companies but which cannot be deduced from financial data alone.
ESG information can also be used as a tool to invest more sustainably. One company’s ESG data can be compared against its peers, and scoring systems can be constructed that rank companies from the most responsible (‘ESG leaders’) to the least responsible (‘ESG laggards’). Portfolio managers can use ESG data to construct more sustainable portfolios, for example by focusing on ESG leaders. ESG investing can create a variety of portfolios depending on the investment manager’s objectives and how ESG information is used in their decision-making process.
Impact investing
Impact investing is not a tool, like ESG, but a more defined investment strategy. Impact investing intends to create a material, additional and measurable positive impact on society. The scope of analysis is larger – while ESG information focuses on a company’s operations (often relative to its peers), impact investing takes a more holistic and absolute approach by evaluating a company’s purpose, as reflected in its core products and services.
Impact investment managers look for companies contributing meaningful solutions to unmet social and environmental needs. In search for a consensus around these needs, impact investors often refer to the 17 UN Sustainable Development Goals as a framework. These Global Goals, adopted by 193 countries, describe specific measures of progress that we must make to tackle our most pressing global problems. The Global Goals guide impact investors’ investment selection and reporting: for example impact themes might include investments in education (Goal 4), renewable energy (Goal 7) or access to healthcare (Goal 3).
Our investment solutions
The EQ Positive Impact portfolios have a dual mandate: maximising risk-adjusted financial returns while making a positive social and environmental impact. They have reflected best practice in the field of active impact investing since their launch in 2012.
A year ago, in March 2020 we launched the EQ Future Leaders portfolios to provide a passive sustainable investment solution. These portfolios use only low cost, passive funds that focus on ESG leaders with additional overweights in selected impact themes.
Both portfolios avoid investments that work against the Global Goals – but they do this in different ways. An active fund management approach (as used by EQ Positive Impact) works by picking out individual companies. By contrast a passive, ESG data-driven approach (as used by EQ Future Leaders) works by ordering and ranking companies across a region or sector. Since the screening process is different, so are the underlying businesses that make up the portfolios.
The diagrams below illustrates the portfolio composition of EQ Future Leaders and EQ Positive Impact:
 The EQ Future Leaders portfolios were launched to provide a sustainable investment solution while keeping underlying fund costs low. On the back of innovation in the index provider space, we were able to construct a portfolio strategy that holds strong sustainability credentials – across ESG, impact themes and carbon footprint.
The EQ Future Leaders portfolios were launched to provide a sustainable investment solution while keeping underlying fund costs low. On the back of innovation in the index provider space, we were able to construct a portfolio strategy that holds strong sustainability credentials – across ESG, impact themes and carbon footprint.
The core of the portfolio is built from regional index trackers, following the MSCI SRI screening methodology – which invest in the top 25% rated ESG performers in each industry after excluding the most controversial ones. We enhance the sustainability by including satellite funds and ETFs that are positively aligned with the Global Goals: currently including healthcare, green bonds, clean energy and water.
 The EQ Positive Impact portfolios are run with a dual mandate: maximising risk-adjusted financial returns while making a positive social and environmental impact. We select specialist impact fund managers that invest in companies whose core products and services contribute towards the Global Goals. Positive impact companies therefore form the core of the portfolio. Naturally, we expect these companies to have responsible operations and strong ESG data.
The EQ Positive Impact portfolios are run with a dual mandate: maximising risk-adjusted financial returns while making a positive social and environmental impact. We select specialist impact fund managers that invest in companies whose core products and services contribute towards the Global Goals. Positive impact companies therefore form the core of the portfolio. Naturally, we expect these companies to have responsible operations and strong ESG data.
We also expect fund managers to engage with their holdings to continually improve outcomes for all stakeholders. It is not yet possible to allocate 100% of investments to solving unmet needs while remaining sufficiently diversified. The remainder of the portfolios is made up of ESG leaders. We constantly strive to maximise alignment to the Global Goals and make progress year-on-year as the investable universe expands.
The table below summarises the key differences in approach:
|
EQ Future Leaders |
EQ Positive Impact |
| Active/passive |
Passive |
Active |
| Asset classes |
Equities & bonds |
Equities & bonds |
| Regions |
Global |
Global |
| Underlying companies |
Targets ESG leaders, diversified across industries. Overweight in sustainable themes. |
Targets impact companies with products and services that solve social and environment problems. |
| Negative screening |
Alcohol, Armaments, Adult entertainment, Fossil fuel extraction, Tobacco, Thermal Coal |
Avoids all in FL, and additionally any industries that prevent progress on the UN SDGs |
| Reporting |
SDG alignment, carbon footprint & climate scenario analysis |
Impact calculator, SDG alignment, carbon footprint & climate scenario analysis |
| Clients |
- Interest in sustainability across sectors.
- Cost concern is greater than sustainability ambition.
- Want to risk-mitigate investments in a changing world.
|
- Want to contribute to solutions to social and environmental problems.
- Strong personal positive and negative sustainability preferences.
|
| Learn more |
EQ Future Leaders online |
EQ Positive Impact online |
How we measure sustainability
Alignment to the UN Sustainable Development Goals
We assess all underlying holdings on whether their core products/services contribute to solutions to the Global Goals, or whether they are negatively impacting on progress.
Compared to market indices, both of our portfolio ranges show significantly higher positive alignment to the Global Goals, and lower or zero negative exposure to these.
As an active investment strategy, EQ Positive Impact has a high level of ambition in this respect, and can avoid investing entirely in a wide range of businesses that could be considered to work against the Global Goals.
As a passive investment strategy EQ Future Leaders also excludes many controversial industries, but retains exposure to some of the most responsibly managed companies (ESG leaders) within some sectors such as mining, or food and drink companies that Positive Impact excludes on health grounds (e.g. alcohol, fast food).
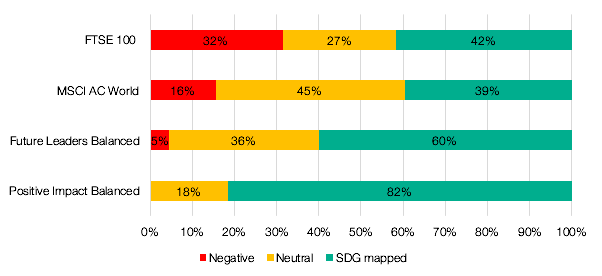 Data: EQ Investors, March 2021
Data: EQ Investors, March 2021
Portfolio carbon footprint
Carbon emissions are the greatest driver of global climate change. Carbon footprinting shows how much of a contribution portfolio companies are making towards this global challenge.
We use emissions data across our portfolio companies’ operations and supply chains (‘Scope 1,2 & 3’ under the Greenhouse Gas Protocol) to create a weighted carbon intensity for each portfolio and market index.
Both of our portfolio ranges have significantly lower carbon footprints than market indices. One reason, common to both portfolio ranges, is that both avoid exposure to the fossil fuel industry. By focusing on ESG leaders, EQ Future Leaders is more likely to invest in companies that are managing their emissions better than their peers. By seeking out those companies providing solutions to global challenges – including climate change – EQ Positive Impact has an even lower carbon intensity overall.
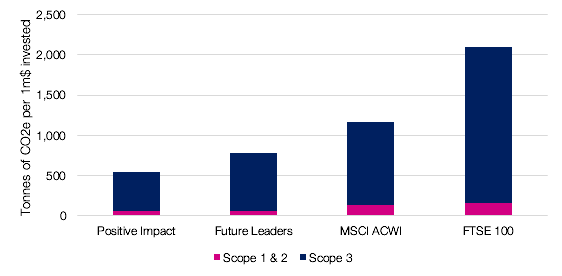 Data: Urgentem, Jan 2021
Data: Urgentem, Jan 2021
If you have any questions on the content or the EQ sustainable portfolio ranges, please be in touch.