The healthcare sector is at the forefront of solving several of the world’s major challenges and market-creating innovation; from adapting to changing demand due to demographic shifts, to developing new drugs and treatments that can radically alter how we deal with diseases.
One of the great hallmarks of the late 20th century was a significant rise in the global population, with the number of people more than doubling from 2.5 billion in 1950 to 5.3 billion in 1990.
In contrast, the 21st century is marked by aging populations and falling fertility rates, leading to rising old-age dependency ratios. If current trends continue, nearly 25% of the global population will be over 60 by 2050 – double today’s share.
Although an aging population isn’t a new phenomenon, recent broad-based declines in healthcare sector valuations suggest the market has been overly pessimistic.
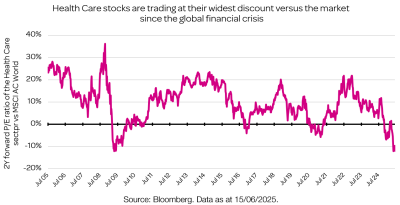
Looking ahead, many companies affected by this valuation drop are well-positioned to benefit from aging demographics, particularly those focused on long-term care and treatments aligned with shifting spending away from hospital-based care.
Additionally, companies focused on preventative care are poised to play a key role in promoting a healthier population, ultimately reducing the need for more intensive healthcare interventions and lowering system-wide costs. At the same time, artificial intelligence introduces a promising new dimension to the sector, offering potential to improve diagnostics, personalise treatments, and enhance overall efficiency across healthcare services.
Technology is already transforming healthcare by enabling earlier disease detection, minimising human error, and streamlining administrative tasks – contributing to better patient outcomes and lower overall costs.
One major area of innovation is in obesity treatments, where portfolio companies like Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly are developing drugs that not only lead to significant weight loss but also reduce risks of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, and hypertension.
Emerging clinical data suggests these treatments may also offer benefits for conditions such as dementia, kidney disease, addiction, and sleep apnoea, highlighting their broad and potentially revolutionary impact on public health.
